Windows 10 Pro and Enterprise edition features the remote desktop utility that allows users to set up and take control of remote desktops without the help of third-party softwares. While connecting to the remote desktop you may notice this error message – ‘Remote desktop can’t connect to the remote computer’. Follow these detailed fixes to solve this problem.
Fix 1 – Check the network connectivity
The most likely reason behind this RDP failure is the network connectivity issue.
Use Telnet client
You can use the Telnet client to check the network. But you have to enable it first.
1. Type “cmd” in the search box.
2. Right-click on the “Command Prompt” and click on “Run as administrator“.

3. Once the Command Prompt appears, type this code and hit Enter.
dism /online /Enable-Feature /FeatureName:TelnetClient
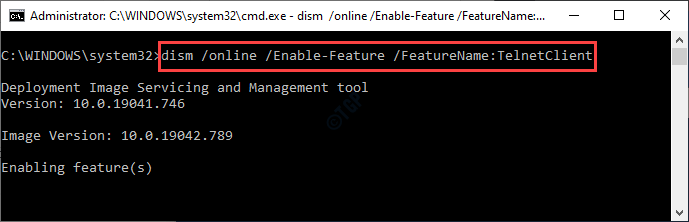
Close the Command Prompt.
4. Press the Windows key+X keys together.
5. After that, click on the “Windows PowerShell (Admin)“.
6. PowerShell with admin privilege will appear. Type or copy-paste this command and hit Enter.
Install-WindowsFeature -name Telnet-Client

After enabling the feature, close the PowerShell window. Then, try to ping the TCP port the remote computer is connected to using the Telnet.
Use PSPing
If the Telnet is causing any problem, you can use the PsPing (it is portable, so no need for installation).
1. Download PsPing portable on your computer. Just click on “Download PsTools” to start downloading.

2. Then, extract the zip file to this default location –
C:\WINDOWS\system32
NOTE–
Extract the files in the directory that is already in your path in the CMD command line.
Example – In this case, the default directory of the command line is at –
C:\WINDOWS\system32

So, we have decided to extract the zip file in that particular location.
3. Now, type “cmd” in the search box.
4. Then, right-click on the “Command Prompt” and click on “Run as administrator“.

5. Once the Command Prompt opens up, type and modify this code according to your scenario and hit Enter.
psping TCP port that your remote setup is connected to
[Change the ‘TCP port that your remote setup is connected to‘ with the specific TCP port that the remote machine is currently using.
Example – The remote setup is connected to the ‘192.168.0.100:2369’ port. So, the command will be –
psping 192.168.0.100:2369
]

6. Now, there are two possible cases here –
CASE A – If the command works out and you face some difficulties pinging the machine using the FQDN name, you have to check if the DNS resolution is properly working out or not.
CASE B – If you can’t connect with the remote setup at all, a local firewall or a network firewall is obstructing the TCP port.
To test out this case, you can disable the Windows Firewall on the remote computer setup.
At first, check what is the status of the firewall on the remote system.
a. Open Command Prompt with administrative rights.
b. Then, copy-paste this command in the terminal. Modify it accordingly and hit Enter.
Invoke-Command -ComputerName [ComputerName] -ScriptBlock {netsh advfirewall show allprofiles}

NOTE –
Replace the “[ComputerName]” with the name of the remote computer you are trying to access.
If you notice that the firewall is ON you can disarm it for testing purposes.
c. You can disable the firewall with a single command. Just paste this code in the terminal and hit Enter.
Invoke-Command -ComputerName Win7 -ScriptBlock {netsh advfirewall set allprofiles state off}

NOTE–
For the efficient function of the above command, you will need the PSremoting turned ON on your remote computer. If it is not, you can use PsExec to turn on PowerShell remoting with this command.
psexec \\RemoteComputer -u administrator -p PASSWORD netsh advfirewall set allprofiles state off

This should fix the connectivity issue.
Fix 2 – Add admin user permissions
If the user account you are using to connect to the remote setup belongs to the non-admin group, you won’t be able to connect via RDP.
1. You have to open the Computer Management. So, press the Windows key along with the ‘R‘ key.
2. Then, type “compmgmt.msc” and click on “OK“.

3. When the Computer Management opens up, right-click on the “Computer Management” on the left-hand pane and click on “Connect to another computer…“.

4. Then, choose the “Another computer:“.
5. Click on “Browse“.

6. Next, click on “Advanced“.

7. To view the list of groups., just click on “Find Now“.
8. Here you will find a list of users and groups. Scroll down through the list of groups or users and select your account name.
(For me, it is “Sambit”. )
9. Click on “OK“.

10. Finally, click on “OK“.

This should be sufficient to manage the remote computer without the need to further credentials if you have logged in to an Active Directory Domain.
This process will only work if the firewall setting allows remote administrative policy exceptions settings is enabled on the system.
If you want to manage the remote setups from the Computer Management, follow these steps-
a. Press the Windows key+R keys.
b. Type “gpedit.msc” and click on “OK“.
c. Once the Group Policy Editor opens up, go this way –
Computer Configuration > Administrative Templates > Network > Network Connections > Windows Firewall > Domain Profile
d. On the right-hand side, double click on “Windows Defender Firewall: Allow inbound remote administrative exception“.

e. Set the policy to “Enabled“.
f. Then, click on “Apply” and “OK“.

Once you have changed the settings, you can manage the remote desktop as an administrator.
NOTE–
If you face any difficulty with Computer Management, you can try an alternate method. But you will need PsTools on your computer.
1. Open an elevated Command Prompt window.
2. Write or copy-paste this code in the CMD screen, hit Enter.
psexec \\ComputerName net localgroup Administrators "DomainName\UserName" /add
NOTE – Replace the parameters in the code according to your case.
Example – For this computer, the ‘ComputerName’ is “MYPC“. My domain name is “Dom1“. The name of the user is “User1“.
So, the command will be –
psexec \\MYPC net localgroup Administrators "Dom1\User1" /add

This will do the trick and add your active directory to the list of administrators. Try to access the remote computer using this account again. Your problem should be solved.
Fix 3 – Allow remote desktop connection
You have to allow the remote desktop connection settings on your system.
1. Press the Windows key+R keys together.
2. Once the Run window comes up, type “sysdm.cpl” and hit Enter.

3. After that, go to the “Remote” tab.
4. Here, check the box “Allow remote connections to this computer“.

5. Finally, click on “Apply” and “OK” to save this change on your system.

Now, try to connect to the remote computer once again.
If this doesn’t work out you can try to enable the Remote Desktop Connection from the Registry Editor.
1. At first, just press the Windows key+R keys together.
2. Then, type “regedit” and click on “OK“.

3. Next, proceed to this location on the Registry Editor screen –
Computer\HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Terminal Server
4. Once you have reached there, double click on the “fDenyTSConnections” key to modify it.

6. Set the value to “0“.
7. Click on “OK“.

This should enable the Remote Desktop Connection. Check the status of the problem again.
NOTE – A
If you can’t toggle either the settings or the registry editor, you can run this Powershell code to do the same.
1. Open the PowerShell terminal with administrative rights.
2. Then, run this simple command to alter the registry value.
(Get-WmiObject Win32_TerminalServiceSetting -Computername [ComputerName] ‑Namespace root\cimv2\TerminalServices).SetAllowTsConnections(1,1)

NOTE – B
There is another process to alter the registry value. But it requires the Remote Registry service in running state to function properly.
1. Open an elevated command prompt screen with administrative rights.
2. Then, paste this command in the terminal and hit Enter.
REG ADD "\\[RemoteComputer] \HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Terminal Server" /v fDenyTSConnections /d 0 /f /t REG_DWORD

[Don’t forget to alter the ‘RemoteComputer’ according to your case.]
Try to connect to the remote desktop once again.
Fix – 4 Check the status of the RDP services
Some Remote Desktop Protocol services are required to be running at the back on both the local computer and the remote computer.
1. Press the Windows key+R.
2. Type “services.msc” and click on “OK“.

3. Once the Services screen appears, check for the “Remote Desktop Services“. Double click on it.

4. Then, set the ‘Startup type’ to “Automatic“. Click on “Start” to start the service.

5. Click on “Apply” and “OK” to save the changes.

6. Same way, double click on the “Remote Desktop Services UserMode Port Redirector“.

7. Just like the Termservice, set the startup type of this one to “Automatic” also.
8. Start the service by clicking on “Start“, if it is already not running.

9. To save the changes, click on “Apply” and “OK“.
Make sure you have ensured these changes in both the remote computer and the local computer.
Restart both the machines once to save the changes.
NOTE –
If you don’t want to modify the services from the Services screen, you can do it just by passing a command.
1. Press the Windows key+X keys together.
2. Then, click on “Windows PowerShell(Admin)”.

3. Then, type this code. Modify it accordingly and hit Enter.
"TermService","UmRdpService" | ForEach-Object{ (Get-WmiObject Win32_service -ComputerName [RemoteComputer] -Filter "Name = '$_' ").StartService() }

This will start the service on the remote client. Though, you will need to manually configure the above-mentioned services (TermService and UmRdpService) to startup automatically.
Fix 5 – Modify group policy settings
There is a chance that the group policy is preventing your RDP request.
1. You have to press the Windows key+R keys together.
2. Then, write “gpedit.msc” and click on “OK“.

3. Once the Group Policy Editor opens up, go to this place –
Computer Configuration > Administrative Templates > Windows Components > Remote Desktop Services > Remote Desktop Session Host > Connections
4. Now, on the right-hand side, double click on the “Allow users to connect remotely by using Remote Desktop Services“.

5. Click on the radio button beside “Enabled” to enable the policy.
6. Click on “Apply” and “OK” to apply the settings.

This should fix the group policy settings to permit the RDP requests.
You can check the group policy results with a single command. Run this GPresult code on the remote computer to get the policy update in an HTML format.
1. Open the elevated command prompt.
2. Execute this code –
gpresult /h C:\output.htm

Fix 6 – Test the RDP listener port on the remote machine
Generally, RD service listens on port 3389 as it is the default port to do so. If any other application on the remote machine is using the same port, this problem may appear.
1. In the Remote computer, first of all, press Windows key+R keys together.
2. Then, type “regedit” and click on “OK“.

3. Next, proceed to this location on the Registry Editor screen –
Computer\HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Terminal Server\WinStations\RDP-Tcp
4. On the right-hand side, look for the key “PortNumber“.
5. Notice the value of the key is –
0x00000d3d(3389)

6. If the value is anything different, double click on the “PortNumber” key.

7. Set the ‘Base:’ as “Decimal“.
8. Then, set the ‘Value:’ as “3389“.
9. Click on “OK“.

Then, close the Registry Editor window. Restart the system once.
This will ensure the remote machine uses port 3389. Your problem should be solved.